– Global Population as of 2024 – 8.15 billion human beings
– Indian Population of 2024 – 1.45 billion human beings
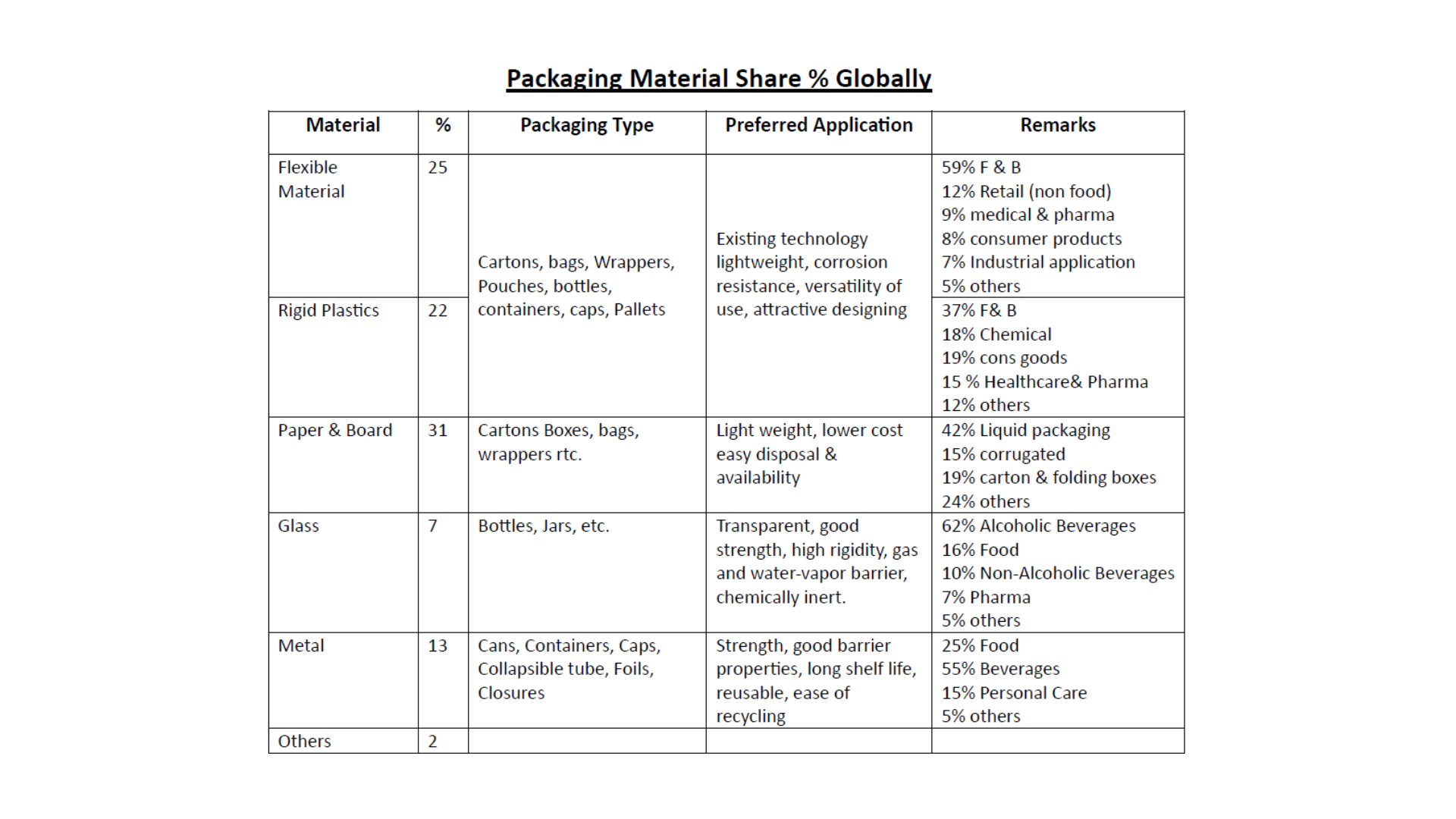
– According to UN, each individual consumes around
Consumption in Kg
Per Person Cost
Global consumption in billion US $
Global – 8.2 Kg
114 US $ (9804) INR
929
Indian – 8.6 Kg
44 US $ (3784) INR
65
-Indian Packaging industry is the 5Th largest in the world which consist of 7% of the global Packaging industry – China and North America is 1st & 2nd
1.China – 276 billion
2.N. America – 203 billion
3.Asia Markets – 129 billion (Ex. China & Japan)
4.W. Europe – 78 billion
5.India – 65 billion
-Packaging growth is directly linked to GDP
-Consumer Segmentation
1.FMCG / FMCD
2.Healthcare / Pharma
3.Personal Care
4.E-Commerce / Retail
5.Industrial Packaging
– However in India Organised retail & boom in e-commerce will offer huge potential for future growth.
– India has 22,000 Packaging units that operates in glass, paper, plastic, metal and corrugation packaging 85% of which is SME.
– Indian Population (Emerging Markets) moving from rural to urban locations and subsequently adopting the westernized lifestyle boost the demand for packaged goods and further this is accelerated by e – commerce
These packaging Companies further focus on four different categories
Raw- Materials
Converting Industries
Machineries
Ancillaries
Overview
Domestic Manufacturers largely control the Indian Packaging Industry, although Some leading global packaging companies have also established a strong presence in Indian market
The visible transaction is around – 80% unorganized share & 20% is the organized share
Key Indian Players
– Global Players – & Global Players presence in India (*)
– Classification of Players in the Primary / Secondary (Indian Players) Packaging segment.

*Note:
Corrugated Cartons,
polybags, bubble wraps etc
Driven by E-commerce, 3PL, Online Grocery & Food Delivery,Electronics, Apparel, Books, Personal Care, Home Furnishings
and other’s)
-Flexible & Rigid Packaging Companies regional & international

Key Packaging Trends:
1. Reduction in packaging materials – thinner, stronger design, lighter, simpler.
2. Packaging cioser to manufacturer – less empty cartons carried in Lorries.
3.Smart packaging – rapid print, aligned with real-time campaigns and offers; more use of
RFID technology for electronic tagging, tracking of stock, as cost of RFID tags falls.
4.Better recycling – easier recycling of packaging, higher percentage recycled materials in
new packaging.
5. Biodegradeable packaging – eg plastics made from starch, more use of cardboard.
6. Space-saving packaging – eg growth of square cartons for drinks.
7. Customer Returns packaging – improvement in re-seal pouches to keep pace with huge growth of online ordering of eg clothes where customers often order several sizes to try
on, returning most goods ordered.
8. Better ways to print branding /marketing on plastics eg bottles.
9. Less use of solvent-based inks for printing.
10. Consolidation of packaging industry – economies of scale with larger machines, faster
turnarounds, next-generation technology
Challenges
1.Competitive Intensity
2. Investments / Rapid Changes in technology
3.Government regulations
4. Shortage and Rising cost of raw material
5. Costly Skilled Manpower
6. Rising input costs
7. Highly inadequate credit flow
8. Lack of Market Access & Advanced technology
9. Lack of exposure to Best Management and Manufacturing Practices
10. Lack of 100% Commitment to the quality standards
11. Lack of Marketing, Distribution and Branding
12. Non-availability of skilled man-power
Summary
Four major trends will change the game in the Packaging industry and raise the bar for Performance in the next 10 years.Much higher level of information and agility will be required to deal with the pressure and potential disruptions emanatory from these trends.
E-Commerce everywhere
– Intense focus on increased packaging requirements, including for new products, along with last mile delivery innovation E- commerce Packaging will meet new and different needs increased requirements for strength & less investment necessary “on the shelf” printing, etc.
The view is that e-commerce will radically diminish the traditional role of primary packaging designated to attract the Consumer’s interest in retail stores as part of the purchase decision and this role would be Reached till 2030 & traditional primary Packaging would be termed as old-fashioned/traditional primary as quaint – relic of the past? & between these period the consumer who is gradually becoming digitally Savvy will seamlessly roam between the both online & offline channels and due to the above they have already made up there mind before ordering or buying, This will imply a large – scale shift to utilitarian protective packaging only. Moreover Consumer tools are being developed for easy replenishment reordering and such tools will tend to reduce impulse purchase by consumers in stares.
The strong growth trajectory in parcel delivery implies demand for individual packaging will increase beneficiary converters that make flexible packaging & corrugation boxes, liners etc. and other protective packaging –
E-commerce packaging demands robustness 3-4 times larger than the traditional standards of packaging & the basic requirement is quite simple- prevent product damage & optimize productivity
In fact many more products manufacturers will be looking to (e-channel enabled packaging) ie merging of primary & Bold Secondary packaging designed to allow direct shipment to consumers without a secondary protective outer layer converter/conversion will need to be more localized or conversion may happen at brand owners in house where converters (Captive) would offer rapid prototyping fast turnaround and new technologies.
Instead, there is much greater need to optimize the packaging for the last mile – shipments, improve the consumer’s unboxing experience, and facilitates easy, efficient returns
– Integrating e-commerce as a key component in any packaging company would be the focus point
– Retail business is slowly shifting from brick & mortar channels to online & mobile shopping which will have a significant impaction packaging needs and the traditional converting value-chain constellations.
Changing Consumer Preferences – Digitization / Internet of Things (IOT)
Customer-facing interactive tools, to convey information & emotion and collect data consumer preferences are shifting towards personalization healthier and affordable products
Paper & board will continue to benefit from e- commerce growth and are ideal for integrating digital & IOT solutions (using QR codes, radio frequency (RFID) ID tags, near field communication (NFC) & so on)
Paper, boards as well plastic will see more of the conveyance of primary & Secondary packaging the above four trends would be a nascent stage till 20230, but then they would potentially become disruptive
Most of the healthy growth is expected from emerging workers (India)
Consumers looking for personalization on packaging different SKU and number of pack sizes, offered in traditional channel to today online with marketplace format which may offer much more SKU (ten of thousands) by augmentation.
The millennial consumers appreciate local manufactured products with gives them greater product safety with positive attributes (good for local economy) their views are not good for the branded FMCG Consumer goods, their beliefs as
– more likely to believe in newer brands seems to be better & innovative than the conventional products
– Prefer to shop independently and specialty stores over traditional chains
– Prefer more likely to avoid buying from the big food companies
– High net worth individuals who are millennials migrates to value/ Private Label & Premium segments putting pressure on the traditional mainstream segments HNI Consumers are becoming aware of health and wellness concerns for obesity desire to stay healthy despite ages heightened sensitizing to food safety, overall fresh produce, health-oriented packages.
Increased Price awareness
Price pressure is a constant of business life, but with a new twist: disposable income is decreasing for the majority of the population in advanced economies. Millennials are poorer than their parents, so these consumes are increasingly focusing on price and their need to economize is felling market share growth of private label products. Cost has historically been king serving as a single most important purchasing factor for packing especially in emerging markets especially Converters has less negotiiality power given their smaller size related to their upstream & downstream cycle.
Packaging digitization to create values directly for FMCG and retailers
– Developing track & trace solutions to enable complete supply chain traceability ( for product recall, food safety, quality tracking, etc.)
– Conducting Continuous integrated demand planning for optimize production runs and inventory using customer and third-party data.
– Digitizing customer interaction to deliver a better customer journey, increase sales and improve service, partiality for small-scale customers.
– Increasing customer collaboration
– Pursuing new area of business with opportunities to serve a broader range of smaller customers (local & loyal) directly and efficiently, developing on e-platform where smaller customers can order.Their packaging directly from the converter and not go through the traditional distributor channel.
FMCG & retail Margin Compression
Consumer’s increased price awareness due to digital shopping channels has enormous downward pressure on retail prices. At the same time input and resource prices (Commodities, labour rates) are expected to increasing the cost of goods sold. The trend towards the automation and digitization of interlinked FMCG manufacturers and retailers require not only additional investment but also write-offs of physical real estate assets, intensifying cost pressures from yet another direction.
The combine effect of these shifts will puts intense relentless pressure on the income of upstream – FMCG manufacturer as well as retailers and if not actively managed these pressure would erode the margin almost entirely. With net profits declining with corresponding pressure passed back upstream to converters. Margin Compression will require strong collaboration between converters & packing customers to developer create solutions to reduce cost without compromising conveniency features and increasing sustainability.
Sustainability requirements increasing at every stop of the value chain
As of today, this is not a bigger challenge for the emerging markets, over the period of time this can be the upcoming challenges to reduce packaging waste by FMCG Manufacturers, retailers & legislators
Most consumers claim to be highly concerned about the environment, governments have started responding to public outcry, mostly revolve around banning single–use plastics,
– Increased recyclability, reusability or compostability of packing material
– The largest and most troubling mismatch is arguably between stated desires for sustainability and consumes willingness to buy. Most evidence indicate that, so far consumer’s willingness extended only to a low premium Even with disruption, all the main consumer packaging trend continue to favor plastics over other substrates in most dimensions apart from sustainability.
The hurdle includes cost weight, barrier, and material properties & currently instead filling lives / automize lines at customer end.
Plastic packaging companies (converter) partnering with customs recycling facilities and research institutes to enable both quality & quantity of recycle plastic feedstock in their packaging – Converters Partnering with IOT spaces- technology to facilitates the customers
The future questions to packaging converter
– Is my current & post investment in innovation in line with shifting consumers trends and e-commerce requirements going forward
– How can we better partner with FMCG manufacturers retailers and suppliers to create stronger and longer-term valued relationships that will faster revenue and profitability growth (ideally for all of us)
– What product and technology level investment converter should be making to deal with increased demand, with regard to packaging as part of product sustainability, what partnering opportunities are there for circular recycling, including renewable materials?
Remarks – Excerpts From
– Osborne or Scamper design checklist
https://www.mycoted.com/Special:Search/Osborn/275-checklist
– Alfred Marshall. Principles of Economics

